After receiving the necessary documents (application form and project presentation), our team will try to review your request as soon as possible, and leading experts will offer the best options for project funding.
Currently, loans for the construction and modernization of factories are rapidly developing, giving the business up to half of the required financial resources.
The global transition to Industry 4.0 requires additional funds to ensure the technical re-equipment of industrial facilities.
This process has accelerated since the pandemic, pointing out the critical importance of digital technology to businesses.
ESFC Investment Group offers flexible long-term investment loans for the modernization of factories / enterprises in Europe, the USA, Latin America, as well as in the countries of the Middle East, North Africa and East Asia.
We provide our corporate clients with a full range of financial, legal and engineering services for the implementation of large projects.
Features of issuing loans for the construction of enterprises and factories
In recent decades, bank loans for the construction of industrial facilities have provided sustainable growth of the world economy, creating preconditions for the introduction of high-tech equipment in many industries, the development of the latest management methods and advanced technologies.The factors listed below highlight the need to intensify investment lending in the developing world:
• Obsolescence of equipment, which leads to high energy and material consumption, reduced quality and competitiveness of products.
• Deficit of internal financial resources for expanding lending activities of banks, which requires a wider attraction of foreign capital.
• Insufficient stock market development in many developing countries, limiting the ability of companies to raise funds.
• Inadequate legislation that complicates the practical application of project finance instruments (PF) with their clear advantages.
Investment loans for the construction of factories are widely used in various sectors, playing a particularly important role in the implementation of capital-intensive projects (mining & processing of minerals, heavy engineering, aerospace).
This financing mechanism can be provided in various forms, helping each company to choose the best option.
Table: Types and purpose of investment loans.
| Bank investment loan type | Form of provision of borrowed capital | Features of the use of borrowed funds |
| Loan for the purchase of fixed assets of the company | Bank loan, bonds and leasing | Mainly construction and expansion of existing production. |
| Loan for the construction and expansion of factories | Bank loan, bond issue | |
| Loan for the modernization of the company's fixed assets | Bank loan, bond issue | |
| Loan for complex project implementation | Bank loan, bond issue, leasing, factoring, project finance | Mostly high-tech and expensive modernization projects. |
| Loan for the development and implementation of innovations | Bank loan, bond issue |
The banking system is designed to cover the shortage of investment funds by mobilizing or attracting free cash resources.
In the course of investment activities, the bank acts as an investor, investing significant financial resources for a certain period in the creation or acquisition of real assets and the purchase of financial instruments in order to obtain direct and indirect benefits.
Investment lending is most often a long-term process that includes a set of financial mechanisms. A feature of investment loans is a clear focus on ensuring a further increase in value through the creation of new production capacity, construction, reconstruction, modernization, as well as securing the ownership of the facility for the borrower.
In the macroeconomic aspect, lending is aimed at meeting the investment needs of industrial enterprises and the economy as a whole.
Low interest rates contribute to the continuous technical re-equipment of the industry.
Organization of investment lending
When making a decision to approve a loan, each potential borrower is assessed according to the relevant parameters and ranked in one of the categories predetermined by the bank.Consequently, the bank determines the portfolio of borrowers according to the degree of risk of lending operations.
Risk management is the process by which a bank identifies risks, quantifies, monitors and controls risk positions, and takes into account the relationship between risks. It is important to establish the purpose of lending, the payback period and the degree of risk of a particular industrial project.
Lending for the construction of enterprises is based on the following principles:
• Determining the feasibility and efficiency of lending an investment project: assessing the return on invested capital based on the cash flow indicator, formed taking into account the net profit and depreciation deductions during the operation of an industrial facility.
• Determination of the real value of invested capital and cash flow, selection of discount / differentiated interest rates in the process of discounting cash flow for investment projects.
• Compliance with the credit policy and internal documents of the bank, coordinating the actions of personnel on work with loan applications and loan portfolio.
• Development of an effective mechanism for assessing and managing investment risks.
• Segmentation of potential borrowers depending on assets, experience of cooperation with the bank and determination of limits, restrictions and lending conditions for each segment.
Financial experts note a close relationship between the volume of bank investment lending and financing of innovations. The experience of the USA, Germany and other developed countries shows that the most effective support for lending to industry is carried out on the basis of a specialized government body with sufficient powers.
Loans for the construction of factories are provided on the basis of the applicant's submission of a forecast of indicators and a business plan, which must contain:
• Strategy and business goals, schedules for their achievement and risk factors.
• Detailed information about managers, including their education, practical experience, knowledge of the industry, age and other important information.
• Description of the products and services that the company plans to provide.
• Assessment of investment needs, taking into account a detailed analysis of a number of macroeconomic, market factors and other aspects.
• Professionally prepared financial forecast of business results for at least a year, including data on estimated income and expenses.

ESFC Investment Group, an international finance and investment company, offers large long-term loans for the construction of factories / enterprises around the world.
We finance heavy industry, construction industry, chemical companies, mining and other sectors.
If you would like to know more, please contact our team anytime for a free consultation. As one of the European providers of innovative financial solutions, ESFC is always ready to help you grow business projects anywhere in the world.
Financing the construction of factories and enterprises on a PPP basis
Financing industrial projects on the basis of public-private partnerships (PPP) is of great importance for the development of many strategic industries, since it allows you to successfully implement capital-intensive projects on favorable terms.A clear system of government guarantees and selection of PPP projects play an important role in the development of the national economy and strengthening of the social sphere.
The most important source of financing for the construction and modernization of enterprises are companies' own funds, local budget programs and bank loans. Thus, the role of bank lending in the development of PPP projects has significantly increased, providing the state and business with new opportunities.
This potential source of financing can play an important role in financing industry, provided that interest rates are kept low and the policies of national banking regulators are prudent.
Financial stability and expansion of the resource base of commercial banks is also a prerequisite for the implementation of large-scale projects of this kind.
The prospects for the system of lending to construction and modernization of industrial PPP projects are associated with the fact that this financial mechanism reduces inflationary risks and promotes the inflow of funds to the most important sectors.
Banks are motivated to lend to PPP projects due to the following factors:
• Improved financial results due to the addition of high-yield investment projects with government guarantees to the bank's loan portfolio.
• Strengthening control over the commercial activities of the borrower at all stages of the implementation of the public-private partnership project.
• Expansion of cooperation with the factory after the end of the first loan repayment, as well as a real chance for the bank to become a co-owner of the business.
The participation of financial institutions in PPP projects can take various forms, including the organization of due diligence with the involvement of qualified experts from various fields, the construction and modernization of factories, the provision of additional advisory services, etc.
All parties to the project receive significant benefits as a result of lending to factories on a PPP basis. In particular, innovative companies get access to cheap long-term loans for modernization and innovative development of production. Commercial banks, in turn, significantly expand their loan portfolio and maintain a high level of liquidity.
The government, through the implementation of such industrial projects, will contribute to the improvement of the investment climate and the growth of confidence in the national currency.
Coordination of interests of the parties in the framework of public-private partnership
The point of contact of the interests of banks and the borrowing company is the lower limit of the return on investment.In addition, when deciding to start a project, an enterprise must take into account internal financial constraints, which include:
• The real cost of borrowed capital.
• The cost of the project, that is, the minimum amount of resources for the full implementation of production, technical and other programs of the enterprise.
• External factors, such as rates of bank loans, conditions for attracting capital from domestic and foreign markets, and the competitive environment.
The profitability of PPP projects should exceed the rate on bank deposits and the profitability of government securities presented for redemption. Business interest in the modernization of factories on the basis of public-private partnership can be actively stimulated through targeted subsidies for R&D, the use of tax incentives and measures of budgetary support for technological modernization.
Governments around the world are increasingly using technology acquisition subsidies through direct budget funding, as well as the creation of regional funds for financing innovation.
Coordination of the interests of the bank and the borrower is ensured in the following ways:
• Ensuring that loan is adequate to meet the actual needs of the factory, in particular the need to maintain liquidity in the face of delays in payments.
• Compliance of the loan currency with the currency of the project's cash flows, as well as protection from exchange rate fluctuations in the countries where the company is present.
• Ensuring that tax incentives are consistent with the importance of loans granted.
• Providing effective government guarantees.

To lend to PPP projects, a commercial bank must have sufficient financial resources.
This depends not only on the effectiveness of the current policy and actions of the bank, but also on the monetary policy of national regulators. To form the resources of the banking system, national regulators use a wide range of instruments, including refinancing, adjusting interest rates, etc.
Sources of additional resources can be the issuance of bonds by the government, the stimulation of investment loans, as well as the intensive use of the released financial resources of other enterprises, for which taxes and customs duties can be significantly reduced.
The second important prerequisite for successful lending for the construction of factories within the framework of PPP projects is the conduct of technical and financial expertise.
This ensures that the costs of the project are in line with the real financial capabilities of the private partner and the government's willingness to provide guarantees.
The basis for the feasibility study of a PPP project is usually the so-called cascade model of cash flows. According to this model, the project generates income, which should cover the costs of maintaining the project (salaries, energy, raw materials, taxes), as well as servicing loans.
Taking into account the interest of banks in the timely repayment of the loan, the lender should become a full participant in the analysis, planning and control of the implementation of the PPP project, which ensures the achievement of its goals.
Some ways to balance the interests of the bank and the borrower are given below:
• Effective legal instruments of banking regulation.
• Strict control and oversight procedures by the national regulator.
• Improving incentives affecting the management of financial institutions.
• Maintaining market discipline and control over banks' performance.
• Interventional measures to regulate the money supply.
• Ensuring proper corporate governance.
In addition, national governments can apply tax incentives to banks for investment and lending activities in order to ensure the reorientation of cash flows to the real sector of the economy.
The result of the coordination of the interests of the state, the bank and the borrower on the basis of PPP is a renovation of the production complex, an increase in productivity, an improvement in product quality and an increase in the investment attractiveness of the country as a whole.
The importance of factory modernization for competitiveness
The capital-intensive modernization of manufacturing facilities has become a major challenge for many governments and companies around the world in recent years.The development of the economy of any country can be called successful only when its strategic sectors and enterprises produce modern and competitive products and increase production capacity to satisfy the market.
The competitiveness of a factory largely depends on the quality of management processes and the competitiveness of products.
So, with the development of market relations, the requirements of consumers for the products they buy on the market also grow.
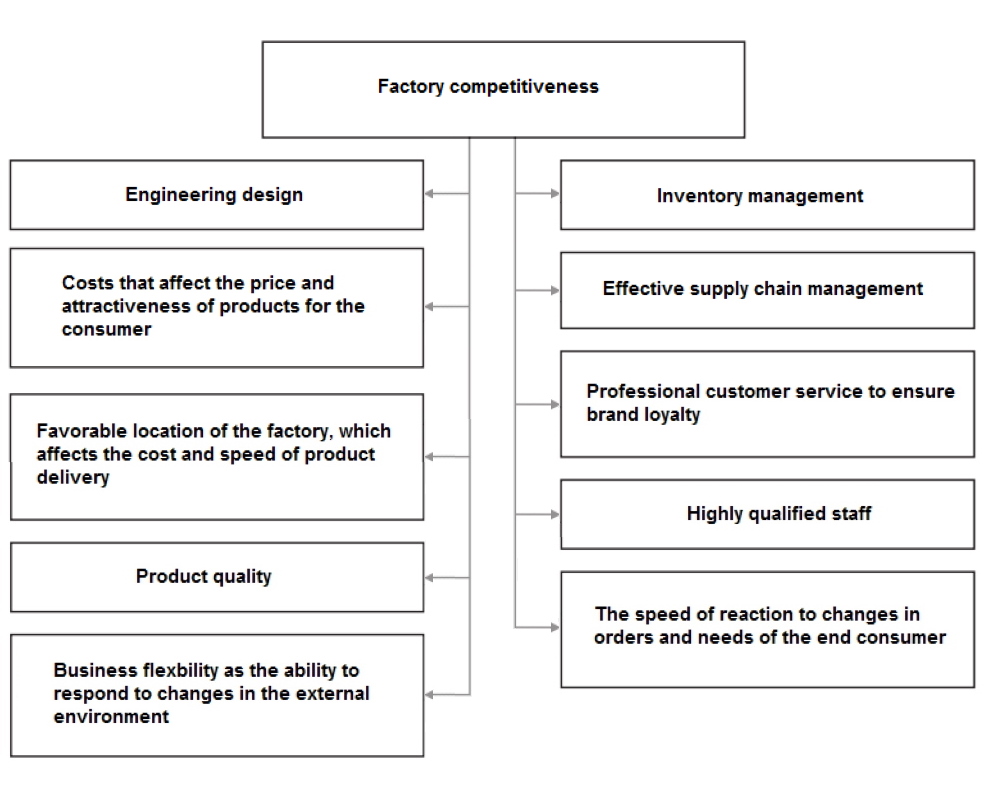
The main task of an industrial enterprise, inextricably linked with production efficiency, ensuring the production of the required amount of high quality products, is to achieve competitiveness of products in the market in the context of continuous implementation of modernization. The competitiveness assessment allows the business to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise, which, in turn, makes it possible to mobilize hidden opportunities to gain a favorable position in the market.
For the successful operation of companies and the achievement of long-term competitive advantages, it is important to use methods that allow not only to measure and maintain, but also to purposefully manage the competitiveness of products.
The management of the competitiveness of products through the modernization of production occupies almost a central place in the general system of enterprise management.
The need for the modernization of factories is due to the influence of a number of external and internal factors. Among the most powerful external factors, financiers name the irreversible globalization of the market and increased requirements for industrial facilities. Only countries that carry out systemic modernization and orient the economy towards increasing the share of innovative products win the competition.
Important measures to accelerate the modernization of factories at the national level should be:
• Establishing the right priorities for the development of the basic sectors of the economy.
• Development of innovative infrastructure, including an increase in the number of innovative enterprises (technology parks, business incubators).
• Creation of favorable conditions for attracting large investments in order to ensure the development of high-tech industries.
These measures can become a solid foundation of state protectionism for the development of high technologies.
Government assistance to modernize factories may include incentives such as tax cuts, postponement or reduction of duties on imported high-tech equipment, etc.
Of great importance for the modernization of industrial enterprises is the implementation of measures aimed at concentrating investment resources on the implementation of innovative programs and projects. Investment loans for factories should be aimed primarily at the technical re-equipment of enterprises in science-intensive and high-tech industries.
Modernization of industrial facilities ensures sustainable and efficient development based on the achievements of technical progress, renewal of equipment and technological processes. The goals of modernization include optimizing the production structure, improving quality, increasing productivity, as well as the widespread introduction of energy efficient technologies and increasing the competitiveness of products in foreign and domestic markets.
It has been proven that competitiveness is influenced by such factors as quality, cost reduction, benchmarking, etc.
The high quality of industrial products means an excellent image of the factory and the company as a whole, the ability to enter the foreign market and receive a stable high income.
At the same time, cost minimization is the traditional and best known method of enhancing the competitive advantages of manufacturing enterprises.
To increase competitiveness, a coordinated work of the personnel is required, associated with the improvement of production technology, the search and implementation of innovations, the improvement of logistics and the optimization of the organizational structure.

The process of forming an effective and competitive structure of an enterprise is characterized as structural modernization, which contributes to qualitative shifts within traditional industries and the formation of new ones. The leading branches of any modern economy are branches where scientific achievements are accumulated.
The acceleration of the global pace of modernization necessitates a clear prioritization within each business, along with the search for the most convenient financial instruments.
The high operating costs and low technical level of production processes that are common in many developing countries require urgent measures for the survival of the business for the foreseeable future.
Sources of financing for the modernization of enterprises and factories
The revitalization of the market for bank financing around the world is gradually leading to an increase in the share of loans for the construction and modernization of factories, but in many countries these processes are not happening fast enough.For this reason, the internal resources of the business remain the key source of financing for the modernization of industrial enterprises.
Self-financing is clearly the dominant source of funding due to the complexity and high risk of borrowing. The reasons for this risk can be different. In developing countries, businesses most often have to deal with an unfavorable investment climate, underdeveloped financial markets and venture financing instruments, as well as with imperfect investment legislation.
Self-financing of the modernization of factories is carried out mainly through the use of profits of enterprises and depreciation deductions.
At the same time, internal financial resources are usually difficult to fully use to finance costly modernization, since these funds must be directed to maintaining working capital, paying dividends to investors and other purposes.
Self-financing of production activities does not allow businesses to timely and efficiently reallocate resources as a result of their cohesion, which causes many structural and technological obstacles. The crisis events associated with the pandemic have led to a reduction in the profits of many industrial enterprises. An acute shortage of domestic financial resources to support current activities contributes to the attraction of borrowed capital, including in the form of bank loans for the modernization of the enterprise and the expansion of production.
External sources of financing for the modernization of factories can be programs of the state and local budgets.
State funding sources are mainly used for the implementation of targeted programs that are strategically and important for the country. Budgetary financing for modernization is usually in the form of interest-free or concessional loans.
The objectives of project financing can be as follows:
• Overhaul and construction of production facilities.
• Refinancing due to the lack of current resources for modernization.
• Financing of changes in the structure of production facilities of the facility.
• Financing an increase in production capacity.
Table: Sources of financing for the modernization of industrial enterprises.
| Debt financing | Equity financing | Asset restructuring | |
| External financing | Bank loans | Participants and founders of the project | Disinvestment |
| Internal financing | Current project costs | Retained earnings of the company | Depreciation deductions |
Industrial enterprises today have a wide variety of alternatives to raise capital.
Of course, it is impossible to provide unequivocal recommendations on the choice of this or that form of financing. In some cases, financial resources should be formed through equity financing, in others - by attracting loans.
The management of modernization projects should use appropriate criteria when making decisions. One of the main tasks of successfully attracting investment in modernization is to substantiate decisions on the choice of optimal project financing instruments for specific financial and economic conditions.
In this regard, enterprises quite often find themselves faced with the need to make informed decisions on the choice of the best existing financial alternative. It can be a choice between loans and internal resources, as well as a choice between issuing bonds and shares (ordinary or preferred).
Table: Comparison of financing models for modernization projects using internal and external sources.
| Criteria | Equity financing | Debt financing |
| The responsibility of capital providers | Full responsibility | Lender status |
| Participation in enterprise management | Usually financing gives the right to manage the enterprise | Usually participation in management is excluded |
| Participation in the distribution of factory profits | The right to participate in the distribution of the company's profits | Usually the lender's rights are limited by the terms of the loan agreement |
| The term of use of funds | Unlimited | Limited by contract |
| Securing debt repayment | Usually not required | Usually provided |
| The tax burden | Debt repayment at the expense of funds remaining after taxes | Interest on the loan is displayed in the balance sheet as company expenses, which reduces the tax burden |
| Debt repayment procedure in case of bankruptcy | The debt is repaid last | Priority repayment of debt to the lender |
An analysis of the world experience in project financing allows us to form a list of the most widely used sources of funds in the order of priority established below:
• Internal resources of the enterprise.
• Bonds and shares (including additional issues).
• Investment loans from banks and non-bank financial institutions.
• Borrowed funds received from open-ended investment funds.
• Targeted loans from international institutions and organizations.
• Government development programs.
• Venture capital, etc.
When making decisions about a loan for a modernization of a factory or alternative sources of financing, it is important to consider criteria that allow assessing the advantages and disadvantages of raising debt and equity capital.

In addition to the above criteria, we note that equity financing is considered less risky for the borrower compared to debt financing.
For the capital provider, on the contrary, the lender status is much less risky, which is due to the peculiarities of the bankruptcy procedure and some other factors.
Leasing as an alternative source of project financing
Leasing is widely used all over the world to modernize factories.It is a profitable alternative to bank lending for technical and technological renovation of machine-building enterprises and other facilities.
Traditional methods of financing industrial upgrades may include purchasing new and used machinery and equipment at own expense, as well as purchasing machinery or equipment at the expense of loans. Against the backdrop of a crisis, with a lack of own funds in many industrial enterprises, banks set higher standards for potential borrowers and require a solid credit history.
Today, many companies are looking for possible alternative sources of financing for capital-intensive factory modernization projects. Leasing can be the answer to new challenges. This financial instrument helps to maintain the competitiveness of the business by simplifying the investment process.
Along with factoring and forfeiting, leasing contributes to the improvement of the company's performance not due to the ownership of assets, but due to their use.
Using leasing mechanisms, the company gets the opportunity to use technical means for the entire or most of the life cycle and overcomes the disadvantages of the above traditional methods of financing.
Leasing as a method of financing the modernization of enterprises has the following advantages:
• The lessor can provide the lessee with different types of services during the term of the lease agreement, which allows the lessee to concentrate on its core business.
• Leasing frees the lessee from potential problems and additional costs associated with the legal side of the project.
• Since the purchase of high-tech equipment requires significant investments, leasing increases the business opportunities of the lessor company.
• The constant nature of payments allows the lessee to plan his expenses and contributes to the greater stability of the industrial enterprise.
• The lessee avoids complicated, time-consuming and expensive procedures associated with assessing creditworthiness and obtaining a bank loan.
• Leasing of technical equipment increases the lessee's liquidity, which allows the implementation of other projects, and also increases the credit rating.
• The lessee retains complete independence, while lending may become for the borrower economic dependence on the lender.
• The lessee records lease payments in the financial statements as operating expenses, which reduces the tax burden on the business.
Industrial trends around the world now clearly show that high competitiveness cannot be achieved by reducing labor costs alone.
To ensure a strong position in the world market, it is necessary to technical renewal of production, as well as the introduction of modern technologies with all their long-term advantages.
Growing competition and tightening global standards require businesses to search for new approaches and mechanisms for project implementation, as well as the introduction of advanced sources of financing for the construction and modernization of industrial facilities.
If you are interested in a loan for the construction, expansion or modernization of a factory / enterprise, contact our financial team.
We provide a full range of financial, engineering, legal and consulting services for large businesses around the world.




























